Localization of autocomponents in Russia failed
26 April 2018
JSC "ASM-holding" considers that the process of localization in Russia in recent years was not there
At the last 25th of April the Moscow international forum "auto COMPONENTS 2018" Deputy General Director of JSC "ASM-holding" Alexander Kovrigin S. in his report entitled "13 years of struggle for localization" told about the vision of your organization on measures to support import substitution and localization of production of automotive components in Russia as in the previous period, and in the near future.

Deputy General Director of JSC "ASM-holding" A. S. Kovrigin
History stages of the target indicators of localization
The famous decree №166 of the Government of the Russian Federation from 29.03.2005 "On amendments to the Customs tariff of the Russian Federation concerning the autocomponents imported for industrial Assembly" was set a target level of localization 30% for both new and existing production (with the only difference for the control period 1-th stage, respectively, 30 and 18 months), which should reach 7 years. For comparison, in China and India at the same time was established much tighter deadlines and a high bar localization – 75% in just 3 years!
What were the results of the implementation "166" regulations for the domestic automotive industry and its component sub-sectors?
The arrival on the market new "players" actually led to the loss of Russia's own automotive industry! Was also lost skilled workforce of designers, engineers, and designers in connection with the winding down of development of domestic models and the transition solely on the Assembly of foreign cars. In this market competed with more than 300 models from more than 50 brands, which led to the dispersal of production to minor quantities, do not provide the ability to localize production.
In the future, when you transition to stage 2 localization was adopted by the order of Ministry of economic development of the Russian Federation No. 678, industry and trade of the Russian Federation No. 1289, of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation No. 184н from 24.12.2010 year. The order formally increased the requirement level of localization to 60% while demand creation capacity of 350 000 cars a year, but the reality was much more depressing. So, not having fulfill previous commitments to foreign manufacturers, at the signing of the new wording came into force on other conditions that, in part, improved conditions of the "old" regulations, although imposed additional obligations, but their execution was actually optional. Moreover, it is clear that they will not be executed properly and by the year 2020.
In life was "introduced" schema "Russian localization", for example, when foreign components with the Certificate of origin in accordance with Article 61 DTS, for example, shafts and gears Inc in collecting from legal entities No. 1 (the importer) did the business No. 2 (the collector) who acted as "producer", whose role was reduced to the elementary operations of drilling and Assembly, but allowed the latter to draw already the Certificate of origin as made in Russia and beyond as 100% of Russian component to put it on the Assembly line of foreign OEM at full cost including VAT. In turn, the OEM reported to the Ministry of industry and trade of the Russian Federation about the reached level of "localization" and allowed him to reduce the volume of imports at a reduced TNVED of the CU. Moreover, upon expiration of the preferential import of individual components, OEM has the right to import all components according to the usual rates of customs duties, constituting 5-15% and almost completely abandon the investment in localization. The focus here lies in the fact that with the exception of HS code TC from the list of preferential positions when imported into the territory of the Russian Federation by foreign OEM, technically, fulfill the requirements to increase localization.
Next, "the miracle continues" – formally, the OEM needs to obtain localised through the local manufacturers of components, and the level of localization had to go up from 15% in the first phase of localization in 2011-2014 of up to 30% in the second phase 2015-2017 and increased to 45% at stage 3 in 2018-2020 However, under the Terms of industrial and technological operations defining concept "Industrial Assembly" of components and assemblies for motor vehicles of headings 8701-8705 HS TS was not given a clear definition of the scope and types of mechanical processing as well as the concept of "degree of localization". In the end, this leads to a dual interpretation of the concepts and complexities of determining the origin of goods. There was no clear definition of manufacturing operations, as well as a clear definition of the percentage of value added at which the goods are considered Russian.
as a result, the OEM, using the scheme with the exception of many items on promsborke benefits, "increased the level of localization", in fact, getting the right accessories through third-party entities despite the fact that the difference in the presence and absence of privileges for industrial Assembly reached, for example, LCV 5,5–7%.
It is also characteristic that in return, the Russian manufacturers of automotive components, was not instituted joint ventures with Russian partners, and in more than 50% of cases – directly daughter of the component companies from the United States.
A. S. Kovrigin said: "One of the most unpleasant scenarios for the Russian automotive industry could become quite a possible limitation of the work of American companies and their subsidiaries in Russia, and this applies not only to the automotive industry. If this happens, we will finally understand how we conduct localization in Russia."
Production facilities across Russia reach more than 3.6 million, but loaded only on 40-50%, so stage 2 localization may remain on paper.
Clean balance of both localization strategies were: active involvement of foreign producers on the Russian market, has invested $23 billion in investment and increase production capacity by 1.7 times, while the number of jobs created amounted to 25 thousand but a price reduction of the Russian platform 3 times (however, quite obsolete – ed.) and underload created capacity by 50-60%. However, the planned increase of level of localization did not happen – her real level did not exceed 30-40%. Low import duties have led to a lack of incentive localizability in Russia, there is no transfer of competences and a large part of the value added leaves the country, creating a negative monetary balance, so every year, Russia exported about $90-100 billion. D the same time, for example, in Germany the automotive industry creates a positive balance for the country, approximately €100 billion.
Problems caused by the introduction of Assembly No. 1 and No. 2 (who is guilty)
1. The decree on industrial Assembly was a colossal mistake, because they were developed unprecedented benefits for low production volumes in 25 000 units per year. It would be right to provide benefits only at the level of production not less than 300,000 units. a year.
2. In the calculation of the first ten projects was that foreign partners have invested $2 billion In reality, it was the related loans, which were mainly spent on the purchase of Assembly equipment in those countries, where the main capacities of foreign partners.
3. Russia has provided benefits in the amount of about $5.7 billion in the form of customs exemptions and tax benefits at both the Federal and regional levels, as well as preferential terms for connection to the grid.
4. Russia lost the most highly qualified engineering and design personnel, because they simply were not needed at the Assembly plants with simplified technology.
5. For the period 2005-2012 was signed around 100 agreements with the manufacturers of automotive components, which actually involved only screwdriver Assembly of parts and components.
6. One of the key disadvantages of all decisions, has blurred the definition of "Russian goods" and supplies components to car factories.
7. The loss to the domestic industry of automotive components in connection with the increase in production of foreign cars in the Russian Federation, and by reducing the number of domestic models in the Park.
8. Only in the automotive industry, the loss amounted to about 500 000 highly skilled jobs.
9. In connection with the high use of imported components like primary production and aftermarket (spare parts), the total amount of money spent for their acquisition, is about $90-100 billion a year. If you take the level of localization in cash, while in 2012 it amounted to about 20%, at present, generally does not exceed 40%.
10. In connection with the unclear wording of the rules of the country of origin, the degree of "sufficient processing" and the liberal policy of technical regulation, it is extremely easy to issue a certificate of conformity for the product, which is considered Russian in the implementation of the basic technological operations, which primarily relates to the automotive subsidiary businesses foreign manufacturers who come to Russia.
11. Currently, completely of the Russian auto component companies are very difficult to certify their products to implement her supplies to the conveyors of foreign enterprises.
the Expected effect of the implementation of the Strategy until 2025
Implementation of the Strategy will provide:
the growth of labor productivity, human capital development, export of engineering services, acquiring new production skills in the automotive industry, the inclusion of domestic manufacturers in the global supply chain, increasing the depth of processing of raw materials.
Implementation of the Strategy will contribute to a balanced satisfaction of the interests of key players in the industry, in particular:
The return of return on investments, ensuring the profitable development of the industry, to increase revenue producers to ₽2.5 trillion annually, increasing the domestic market to 2.5 million vehicles, to increase the level of localization of cars to 70-85%, adaptation of advanced technologies and expertise, increase of competitiveness of production, employment and stability of revenues to ₽150 billion in tax revenues annually.
in addition, the report reflected the level of competitiveness of the Russian economy in 2017, compiled by the chamber of Commerce and industry of the Russian Federation.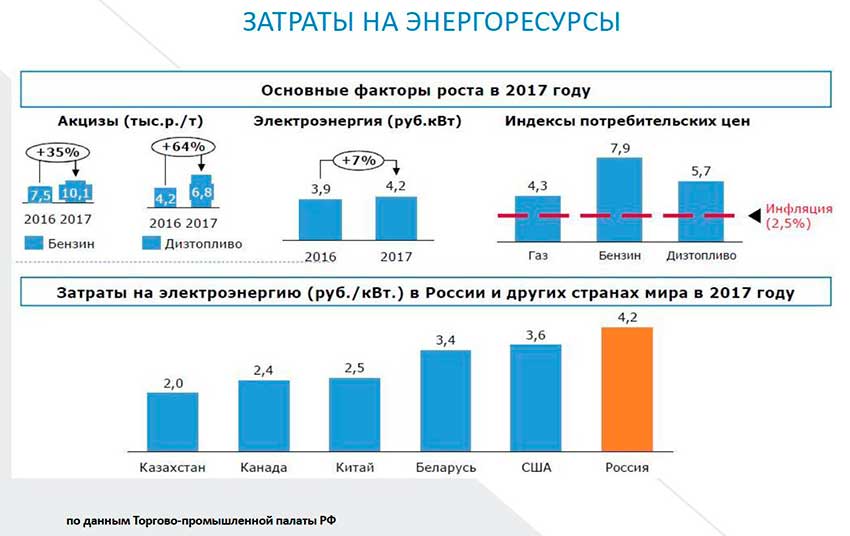
The table shows that in Russia the cost of industry electricity is the highest among the major industrial countries of the world
The same applies to rail and road tariffs (and this despite of our distances), as well as other capital expenditures
It would seem that the level of subsidies is large enough, including on the dynamics of annual growth, but compared to the huge amount of taxes the share of subsidies in fact just miserable
Actual state support of non-oil exports remained purely nominal
Rapid growth of the salaries in the manufacturing industry competitiveness does not increase, although on this indicator Russia lags behind even Brazil
Why could not the localization in the automotive industry (what to do)
1. If we want to create the automotive industry, are encouraged to establish joint ventures, especially in the component industry, which could supply components not only in Russia but also abroad.
2. In the roadmap to be generated, you need a red line to highlight how you will create a new component industry in Russia, if this is not done, then in the future we will become a country that performs primitive assembling the cars from imported components.
3. You must understand that if we aspire to a world in electricity prices, metal, gas and other energy resources, then we will remain a "banana Republic" where, in the best case, it will be profitable to produce and sell energy resources and other natural wealth of the country. Need to move from a promote sales to stimulate production.
4. Reducing the cost of metal, plastics and other primary materials, through measures of state support.
5. The preferential lending component of SP at the rate of 7-8% at present, with a subsequent decrease to 4-5%.
6. Exemption from VAT in the first 2-3 years, products manufactured by these joint ventures.
7. Duty-free procurement of new technologies, licenses and equipment in the first 2 years.
8. Exemption of joint ventures for 5 years from all taxes, except for social.
9. The goal of these activities is to ensure that the products issued by joint ventures was competitive.
10. At the same time should be raised to 30-35% customs barriers for the import of components for enterprises operating on a General basis.
The creation of joint ventures on the "Option 1" is the best way that will allow the parent plant of the Russian Federation to develop technology and replicate the design with further improvements in the same components in the product line of the plant.
Under certain agreements may take place and the "Option 2"
"Option 3" – is totally unacceptable, sobecause it does not allow the transfer of technology to the Russian company, but, at the moment it really is basic in the organization of production foreign partner. This option is a major strategic mistake.
|
|
|
Element was not found.








